Placing a TV or PC (LED Display) in a cold, outdoor or indoor environment can potentially cause damage to the display.
Most TV manufacturers recommend operating above 40°F and storing above 5°F. The LCD or LED screen of a TV is made of
liquid crystals that can freeze and expand when exposed to low temperatures, potentially causing the screen to crack
or shatter. The cold can also affect internal components such as circuit boards, the power supply, and speakers.
In order to protect a TV operating or being stored in cold temperatures, three key measures should be taken:
Keep it Covered, Keep it Dry, Keep it Warm. Protect Your Outdoor TV from Bad Weather: Here are 3 Tips.
Insulation
The thickness of insulation can vary but is typically determined by the space available inside the enclosure.
EPS rigid foam board with a thickness of ½″ to 1″ and an R-value of R2 to R4 works well.
R-Tech Foam Board is a typical product meeting these specs.
Heater Sizing
When determining heater size, a rule of thumb is 100 W per 1 sq ft of internal volume. The TV itself is the first heat
source to consider: most of the power it consumes is dissipated as heat. For example, a TV rated at 125 W will
provide approximately 125 W of heating when operating.
Case Study
PC Enclosures provided several outdoor TV enclosures for the City of Detroit M1 rail system. The TV was 32″, the internal
volume was 1.6 sq ft, the enclosure was 304 stainless steel with a ¼″ polycarbonate window, and it was insulated with
½″ R2 foam board.
To test cold performance, tests were run in a walk-in freezer at 0°F. The TV drew 125 W and a 100 W heater was used,
with a small fan (4 cfm) at the louver to simulate wind.
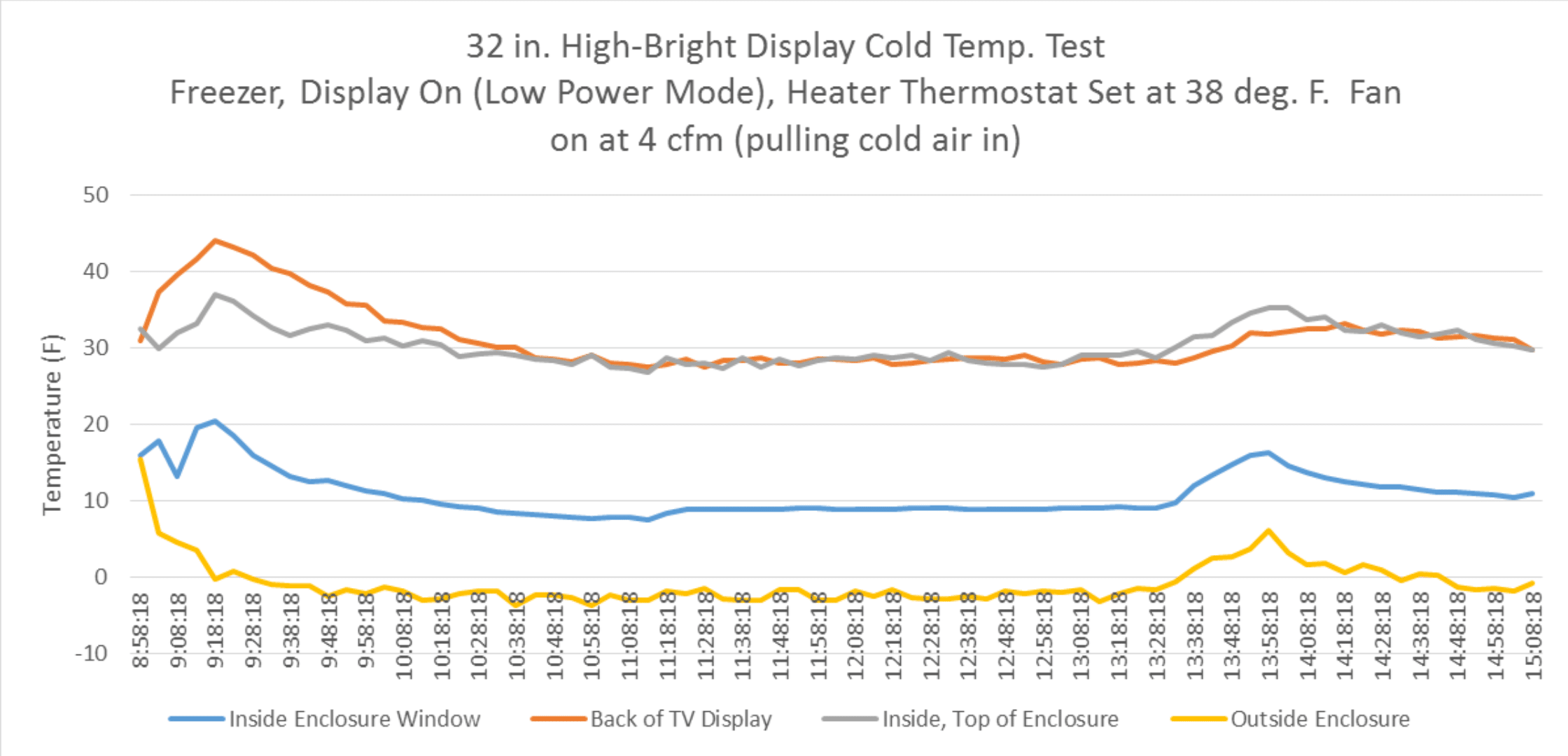
Figure 1 – Cold Test
In this scenario, the 100 W heater maintained about 30°F above ambient behind the TV and about 10°F on the front.
Most heat loss occurs through the polycarbonate window, which is critical when designing the heater.
In a second test, the TV and a DVD player ran together. With the heater thermostat set to 65°F, the combined heat
output (~300 W) was tested. Figure 2 shows these results.
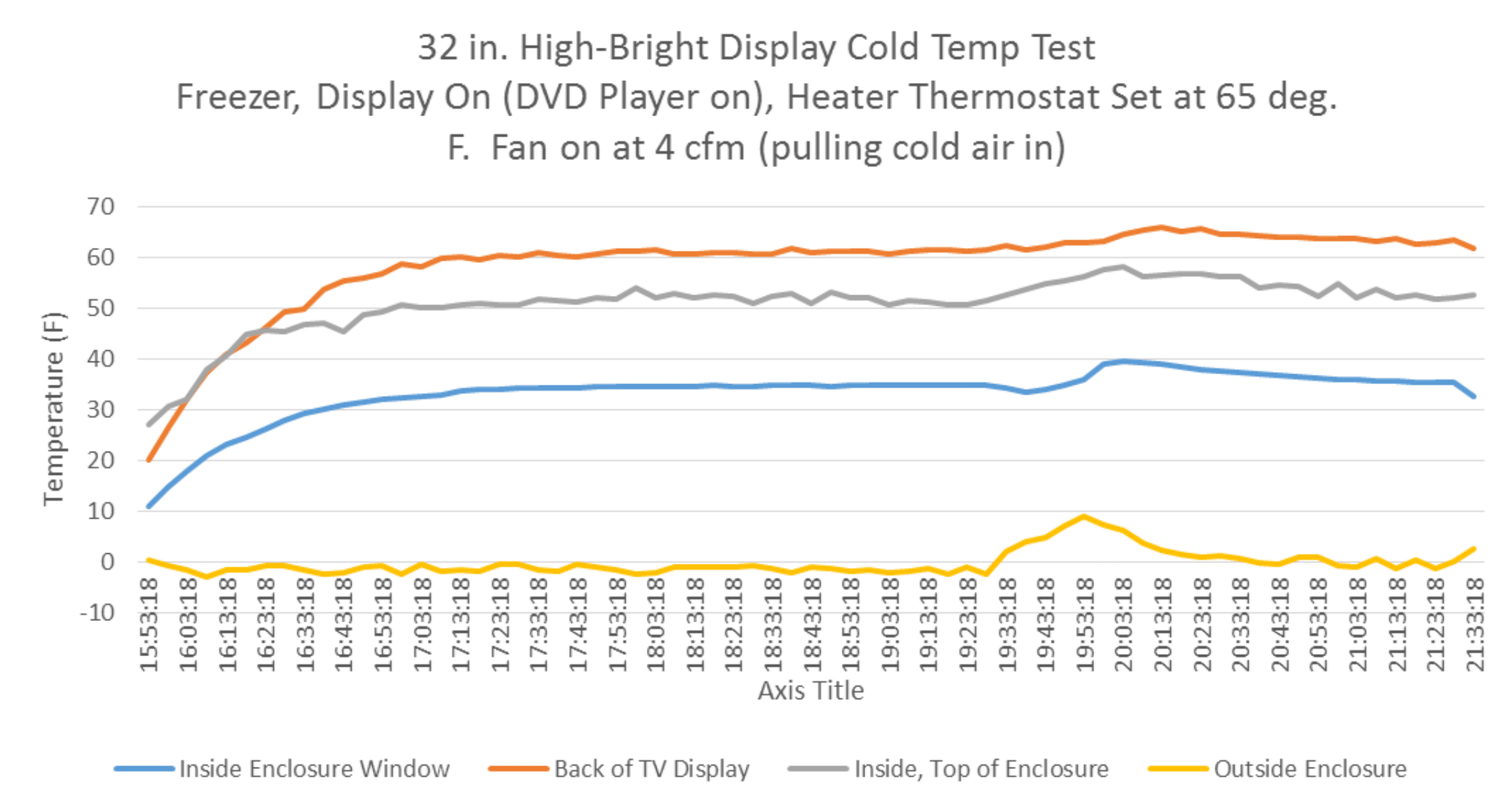
Figure 2 – Cold Test #2
The 300 W of combined heating kept the back of the TV about 50°F above ambient and the inside of the window about 35°F above ambient.
Conclusion
When deploying TVs in cold environments, a heated and insulated enclosure is essential. The TV provides baseline heating,
but additional heat is often required. A good starting point is 100 W of heating per 1 sq ft of internal volume.
















